Today’s Currency Rate in Pakistan – January 7, 2025
The currency exchange rates in Pakistan, particularly the value of the Pakistani Rupee (PKR) against major global currencies, are a crucial indicator of the country’s economic health. As of January 7, 2025, the Pakistani Rupee has shown a consistent performance in the foreign exchange markets, reflecting both challenges and opportunities in the country’s economic landscape. This article delves into the details of the current rates, the underlying factors driving them, and the impact of these rates on various sectors of the economy.
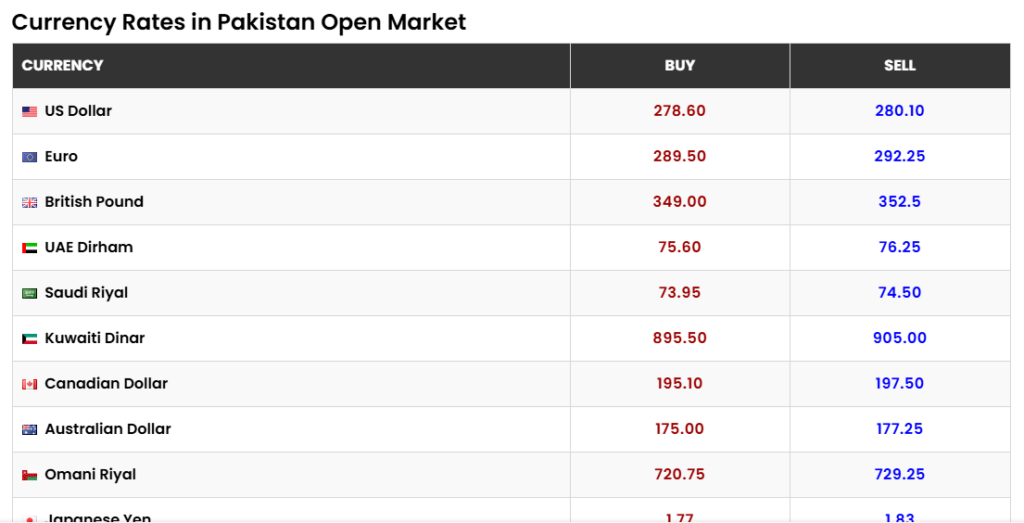
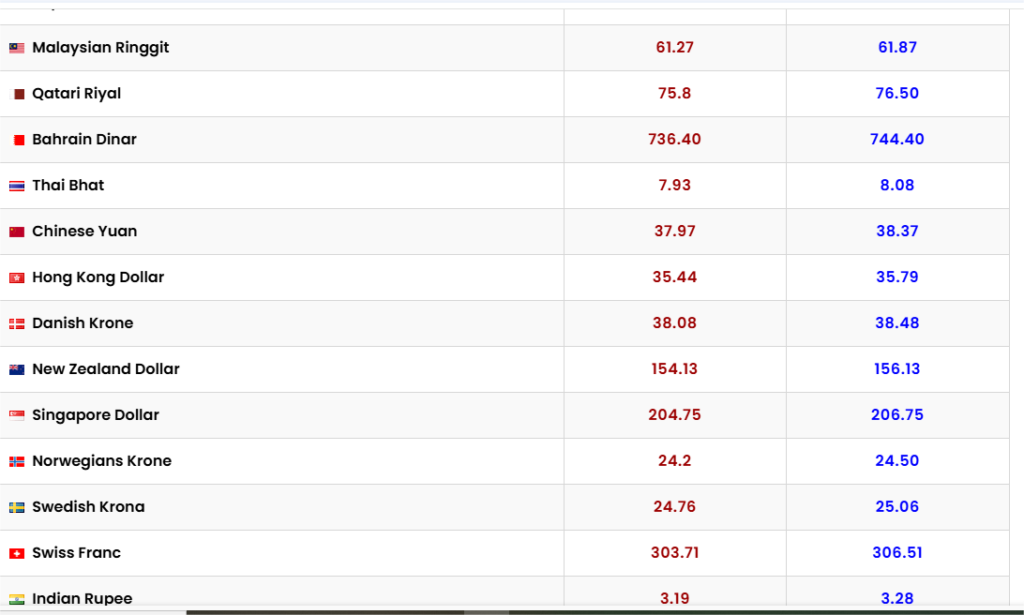
1. Overview of Current Currency Exchange Rates
The value of the Pakistani Rupee against major currencies such as the US Dollar (USD), Euro (EUR), British Pound (GBP), and regional currencies like the UAE Dirham (AED) and Saudi Riyal (SAR) highlights the dynamics of trade and financial flows.
US Dollar (USD) to PKR
- Interbank Rate: Rs278.45
- Open Market Rate: Buying at Rs278.10 and selling at Rs279.80
Euro (EUR) to PKR
- Interbank Rate: Rs288.75
- Open Market Rate: Buying at Rs288.75 and selling at Rs291.50
British Pound (GBP) to PKR
- Interbank Rate: Rs348.00
- Open Market Rate: Buying at Rs348.00 and selling at Rs351.50
UAE Dirham (AED) to PKR
- Interbank Rate: Rs75.50
- Open Market Rate: Buying at Rs75.50 and selling at Rs76.15
Saudi Riyal (SAR) to PKR
- Interbank Rate: Rs73.80
- Open Market Rate: Buying at Rs73.80 and selling at Rs74.35
These rates represent a relatively stable performance of the PKR, with minimal volatility in recent weeks.
2. Factors Influencing Exchange Rates in Pakistan
Currency exchange rates are influenced by a myriad of factors ranging from domestic economic policies to global market trends. Below are some of the key determinants of the current rates:
A. Monetary Policy
The State Bank of Pakistan (SBP) plays a central role in stabilizing the Rupee through its monetary policy interventions. By adjusting interest rates and implementing measures to control inflation, the SBP influences the supply and demand for foreign currencies in the domestic market.
B. Foreign Exchange Reserves
Pakistan’s foreign exchange reserves act as a buffer against currency volatility. A healthy reserve level ensures the country can meet its import and debt obligations, reducing pressure on the Rupee.
C. Trade Balance
The balance of trade, or the difference between exports and imports, is a critical factor. A trade deficit, where imports exceed exports, exerts downward pressure on the Rupee as more foreign currency is required to pay for imports.
D. Remittances
Remittances from overseas Pakistanis are a significant source of foreign exchange inflows. Stable and growing remittances help support the Rupee by increasing the supply of foreign currency in the market.
E. Political Stability
Political stability is a crucial determinant of investor confidence and economic performance. Uncertainty can lead to capital flight and increased demand for foreign currencies, weakening the Rupee.
F. Global Market Trends
Global factors, such as changes in oil prices, interest rates in major economies, and geopolitical developments, also impact the Rupee. For instance, an increase in oil prices raises Pakistan’s import bill, affecting the currency’s value.
3. Impacts of Currency Stability on the Economy
The relative stability of the PKR has far-reaching implications for various stakeholders, including businesses, investors, and the general public. Let’s examine these impacts in detail:
A. For Businesses
- Importers and Exporters:
Stability in exchange rates allows businesses to plan their financial transactions with greater predictability. Importers benefit from stable costs for goods and raw materials, while exporters can negotiate contracts with confidence, knowing the expected returns. - Manufacturing Sector:
Many manufacturers rely on imported machinery and raw materials. A stable Rupee helps control production costs, enabling competitive pricing in both local and international markets.
B. For Investors
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI):
A stable currency is a key factor in attracting foreign investment. Investors are more likely to commit capital when they perceive minimal currency risk. - Local Investments:
Domestic investors also benefit from stability, as it reduces uncertainty in financial markets, encouraging investment in stocks, bonds, and real estate.
C. For the General Public
- Inflation Control:
Currency stability helps control inflation by keeping import prices steady. This is especially important in Pakistan, where a significant portion of consumer goods is imported. - Cost of Living:
A stable Rupee ensures that essential items, including fuel, food, and medicines, remain affordable for the average citizen.
D. For the Government
- Debt Servicing:
A stable currency reduces the burden of foreign debt repayments, which are often denominated in US Dollars or other major currencies. - Policy Implementation:
Economic stability provides the government with the flexibility to implement long-term development projects without the immediate pressure of managing currency fluctuations.
4. Challenges to Maintaining Currency Stability
While the current stability of the PKR is commendable, it is not without challenges. The following are some of the hurdles that need to be addressed:
A. Persistent Trade Deficit
Despite efforts to boost exports, Pakistan continues to face a trade deficit. Addressing this imbalance is crucial to reducing reliance on foreign currency inflows.
B. External Debt
The country’s growing external debt poses a risk to currency stability. Servicing this debt requires substantial foreign exchange reserves, which could strain the Rupee in the long term.
C. Volatility in Global Markets
Global economic conditions, such as fluctuating oil prices and interest rate hikes by major economies, can impact the PKR. Maintaining resilience in the face of these external shocks is essential.
D. Structural Economic Issues
Structural issues, such as a narrow tax base and reliance on a few export products, limit the economy’s capacity to generate sustainable foreign exchange inflows.
5. Strategies for Strengthening the Rupee
To ensure the long-term stability of the PKR, policymakers must adopt a comprehensive approach that addresses both immediate and structural challenges. Key strategies include:
A. Boosting Exports
Diversifying export products and markets is essential. Providing incentives to exporters, improving infrastructure, and ensuring access to global markets can significantly enhance export performance.
B. Encouraging Remittances
Policies that facilitate and incentivize remittances through official channels can increase foreign currency inflows.
C. Managing Imports
Reducing dependency on non-essential imports through local production and consumption can help narrow the trade deficit.
D. Enhancing Foreign Exchange Reserves
Building and maintaining adequate foreign exchange reserves provides a safety net against currency volatility.
E. Promoting Investment
Creating a business-friendly environment, simplifying regulatory processes, and ensuring political stability can attract both domestic and foreign investment.
6. Looking Ahead: The Future of the PKR
The future of the Pakistani Rupee depends on the country’s ability to navigate both domestic and global economic challenges. While current stability is a positive sign, maintaining it requires sustained efforts across multiple fronts. Key areas of focus should include:
- Economic Reforms:
Structural reforms to enhance productivity, diversify exports, and improve tax collection are critical. - Global Integration:
Strengthening economic ties with trading partners and participating in regional trade agreements can boost foreign exchange earnings. - Technological Advancements:
Leveraging technology to improve efficiency in industries and services can enhance competitiveness, driving economic growth and currency stability.
7. Conclusion
As of January 7, 2025, the Pakistani Rupee stands as a testament to the country’s resilience in the face of economic challenges. Its stability against major currencies reflects a combination of prudent policies, steady remittances, and a cautious approach to foreign exchange management. However, maintaining this stability is an ongoing process that requires addressing structural weaknesses, adapting to global trends, and fostering a robust economic environment.
For businesses, investors, and the general public, the current stability offers a foundation for growth and development. By continuing to build on this foundation, Pakistan can pave the way for a stronger and more resilient economy in the years to come.
